An incredibly important aspect of any build or prebuilt PC purchase, memory constantly stores and provides access to temporary data to assist components such as your processor and graphics card in completing their tasks.
Whether you're researching for a new PC build, buying a prebuilt custom PC or need a relatively low cost upgrade, RAM is a popular way to increase performance without swapping out major hardware, and can always offer a boost in application and gaming speed. With hundreds of fast DDR4 and DDR5 options, your RAM selection is essential but can be quite complex. This guide will explain the various specifications and types of RAM available, and how to choose the right memory for your needs.

RAM stands for Random Access Memory, a component in a PC that stores data short-term for quicker access. A computer loads game files, applications or documents you request usually from your SSD or HDD storage into RAM, then accesses each piece of this data from memory as it is needed. Many of the day to day operations of a PC are dependent on memory, the the speed and capacity of RAM is critical for overall performance.
An easy way to see if your PC is ready for a memory upgrade is with your Task Manager, built-in to Windows. Simply hold down the keys CTRL + SHIFT + ESC or hold CTRL + ALT + DEL and select Task Manager.
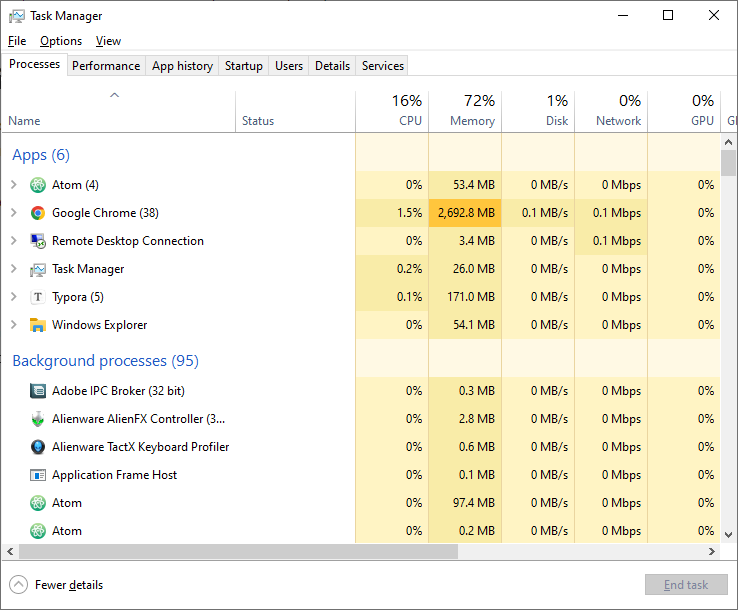
As you can see from the above screenshot, having many active tabs open in Chrome is taking up a lot of memory (the darker orange highlighting shows this). At the top, we can see 72% of available memory is being used.
In this case, the user could use Chrome's built-in task manager to close down processes they're not using (Chrome Menu > More Tools > Task Manager), or clear browsing data, but if this was required on a regular basis, or other tasks were needed at the same time, then a memory upgrade would be wise.
If you ever get too close to 90% - 100% of your RAM availability, you will notice that some applications, files and games begin to load slowly. An upgrade of RAM, in this case, will increase performance overall.


DDR5 is a relatively new technology, and offers a significant improvement in specification over the previous generation, DDR4 RAM. The theoretical performance offers data transfer up to 38.4 Gigabytes per second (GB/s), which is 50% faster than DDR4 at 25.6 GB/s.
These theoretical maximums will be closer to actual performance in hardware releases such as Raptor Lake CPUs and AM5 motherboards from AMD, as motherboard and processor combinations at launch were very close to DDR4 performance in benchmarks (within 5% - 10% increase).
The data rate of DDR4 ranges from 1600 to 3200, and DDR5 offers 4800 to 6400 - twice the data rate per clock cycle. This is displayed as the MHz in specifications (e.g. 4800MHz). DDR5 RAM also has a prefetch buffer size that up to 16n, twice that of DDR4 at 8n. This means DDR5 can read data twice as fast as DDR4.
When new memory releases, the infancy often means the technology available and the price makes it unattractive. That said, if you are using your PC for professional work, competitive gaming, creative workloads, or you need longevity frm your PC, then DDR5 offers you a chance to future-proof your specification. As DDR5 support increases with CPUs and motherboards, and as developers test more on the technology, we will see greater gains overall. If you want a system that will last many years and have a very clear upgrade path, then DDR5 is the way to go. By opting for a next=generation motherboard and processor that supports DDR5, you are adopting the technology we are moving towards, rather than leaving behind.
For older motherboards, DDR3 RAM is still available, but offers lesser performance. DDR3 RAM will only work in DDR3 compatible motherboards, and is not compatible with DDR4 motherboards.
The actual speed of your RAM is determined by three factors:
Frequency or clock speed is a linear factor, in that increasing it simply means increasing performance. By increasing the frequency, you are increasing the memory's bandwidth (the amount of data transferred during a task).
Latency is defined as CAS (Column Address Strobe or Signal) or CL (CAS Latency). Lower CL decreases the time it takes for RAM and a processor to communicate. Low CL = faster communication.
Memory channels depend on your processor and the number of RAM modules (sticks of RAM) you have installed. If you have two or four sticks of RAM, they operate in dual-channel mode, meaning higher memory bandwidth. With a single module, RAM runs in single-channel mode, with lower memory bandwidth.
Whilst all of this may seem complicated, the important takeaway is this: -
Use dual-channel memory (two to four sticks of RAM) with high clock speed (MHz), and low CL RAM in your setup.
To ensure you are getting the best performance from your RAM, however, it is important to tune your frequency and memory timings using XMP. By enabling XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) you are overclocking your RAM to safe levels without having to look up settings or use any third party tweaking apps.
To enable XMP, simply access your BIOS, and locate the XMP menu. Generally, you will see two profile options for DDR4 and three profile options for DDR5 memory. These profiles are set up by the RAM manufacturer, and are safe overclocking levels. Simply select an XMP profile, save and restart your PC. Your motherboard will now use this new profile, and you will see an increase in performance.
High speed CL16 DDR4 RAM:
High speed CL36 DDR5 RAM:
High speed CL38 DDR5 RAM:
View All DDR4/DDR5 RAM:

Yes. We offer various finance options, with flexible payments depending on the price of the memory.
CCL Computers
Inmoor Road
Birkenshaw
Bradford
BD11 2PS





Copyright © 2025 CCL Computers
Grab yourself a great deal...