What is FreeSync?
AMD FreeSync™ leverages industry standards like DisplayPort™ Adaptive-Sync which can deliver dynamic refresh rates on compatible monitors.
With AMD FreeSync technology, the refresh rate of a display is synchronized with the framerate of FreeSync compatible graphics cards, reducing or eliminating visual artifacts that many users are especially sensitive to: input latency, screen tearing, and stuttering during gaming and video playback. AMD FreeSync technology can be delivered through DisplayPort and HDMI® connections. – AMD
AMD FreeSync (all tiers) is supported by over 1700 monitors.
By comparison, Nvidia G-Sync (both tiers) is supported by over 270 monitors.
FreeSync is based on VESA's Adaptive-Sync technology, an open and free technology.
What Is AMD FreeSync Premium / FreeSync Premium Pro?
The three tiers are - AMD FreeSync, AMD FreeSync Premium, and AMD FreeSync Premium Pro.
These three standards are set by AMD, and have parameters that need to be met to classify in each tier.
FreeSync
FreeSync Premium
- Low latency
- Tear free
- LFC
- At least 120 Hz at minimum FHD resolution
FreeSync Premium Pro
- Low latency
- Tear free
- LFC
- At least 120 Hz at minimum FHD resolution
- HDR hardware support
- Wide colour gamut
- Broad contrast spectrum
Depending on the style of gaming you prefer, you can select a FreeSync standard that matches. By checking the optimal settings for your favourite game, you can choose a monitor that offers the specification to get the best experience possible.
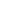
For example, Call of Duty Warzone notes in their specifications that a high refresh monitor is required for “Competitive” experience, and to run in “Ultra”, you’ll be needing a 4K monitor and high refresh rate:
FPS: Frames Per Second. Monitor refresh rate is determined by your monitor’s hardware. Frame rate is determined by the settings in game, and then by the GPU, which then sends this information to the monitor. The framerate of a game can be higher than your monitor's refresh rate but results in screen tearing without FreeSync. FreeSync will ensure the frame rate matches the refresh rate and ensure the GPU does not send excess frames.
What is DisplayPort Adaptive-Sync?
DisplayPort Adaptive-Sync enables a monitor display to dynamically match the rendering rate from the GPU - on a frame-by-frame basis – which results in a smoother gaming experience and has the added benefit of low latency.
Low Latency: Essential for pro gamers, but also general consumers who play games regularly, low latency is a feature on modern monitors; the amount of time it takes for an image from a GPU and being displayed on a monitor. Generally, 15ms (15 milliseconds) or less is preferred for optimal gaming performance.
Why Do I Need FreeSync?
With a compatible GPU (Graphics Processing Unit or graphics card) and monitor, you will see a massive reduction in screen tearing (often eliminating them entirely) and have variable refresh rates at your disposal for low latency gaming.
Screen Tearing: a visual artifact and discrepancy in video display whereby a display device such as a PC monitor will show information from multiple frame draws appearing in a single screen draw. Screen tearing may also happen because of synchronisation (sync) issues between two equal frame rates and will display the tear as a location of the phase difference.
Variable Refresh Rates (VRR): VRR allows a monitor or display device to dynamically alter the refresh rate based on the information from a GPU or other output. Refresh rates on the display change “on the fly” to match the video being sent.
AMD FreeSync – Is It Worth It?
As a feature on a monitor, you will not pay a premium for having FreeSync support. You will find many supported monitors priced under £100, and even sub-£75 for smaller monitor sizes.
With over 1700 AMD FreeSync supported monitors, you have a massive range to choose from, so this makes it easier to balance budget with specifications.
As far as gameplay, you will have an improved refresh rate, low latency and a smoother gaming experience overall when using your AMD GPU with a monitor that has FreeSync support.
In the above image we can see screen tearing as the player’s character turns in the game. FreeSync works to reduce these artifacts by varying the refresh rate as needed, on the fly.
AMD FreeSync vs. G-Sync
As two competing VRR technologies, there is nothing to separate them on the surface. Both features do exactly what they say on the tin and are a massive improvement over V-Sync. That said, if we look at the sheer number of AMD FreeSync compatible monitors, Nvidia’s technology is behind in scaling out their support.
Nvidia G-Sync works by utilising a chip that is installed in the hardware of the monitor (which explains manufacturers’ reluctance to support G-Sync), and AMD FreeSync uses the graphics card’s functionality to adapt refresh rates using information passed through Adaptive Sync in DisplayPort connections.
From a price perspective, G-Sync monitors tend to have a higher price, whereas FreeSync hits every price bracket across the spectrum.
V-Sync: A technology developed by GPU manufacturers to combat screen tearing and refresh rate issues in modern gaming. V-Sync forces a graphics card to wait until the display (monitor) is ready to display the next frame to eliminate screen tearing issues. However, this can result in input lag if the GPU is unable to render an image by the time the monitor is ready for the next refresh.
“Vertical Synchronization (VSync), helps create stability by synchronizing the image frame rate of your game or application with your display monitor refresh rate. If it's not synchronized, it can cause screen tearing, an effect that causes the image to look glitched or duplicated horizontally across the screen.” (Intel)
Input Lag: The amount of time between a keypress or button press and an action on a display. TechRadar’s Jeremy Laird explains: Input lag is “a measure of the delay between signal output from a source device, such as a games console, set top box or PC, and the video image being shown on the display. And it’s all about feel. Does the screen respond quickly to your control inputs in a game? If it does, it has low lag or latency. If there’s a noticeable delay between wiggling a mouse or control pad and on-screen movement, then it probably suffers from significant lag.”
Final Word
Is it worth it? Absolutely. FreeSync was developed to enhance the user's gaming experience, and does exactly what is says on the tin. AMD recognise that such features should be made available to users at every level of budget, too, which is why you can still benefit from better visuals at the cheapest end of the monitor ranges.
With increasingly better inter-technology relationships between AMD and Nvidia, the future holds plenty of promise in terms of compatibility, and the gamer will continue to benefit. Whenever you begin shopping for a new monitor, you should absolutely consider FreeSync as an option.